Cymhwyso microsgop llawfeddygol deintyddol wrth drin clefydau mwydion a pheriapical
Microsgopau llawfeddygolmae ganddyn nhw'r manteision deuol o chwyddo a goleuo, ac maen nhw wedi cael eu defnyddio yn y maes meddygol ers dros hanner canrif, gan gyflawni rhai canlyniadau.Microsgopau gweithredufe'u defnyddiwyd a'u datblygu'n helaeth mewn llawdriniaeth ar y glust ym 1940 ac mewn llawdriniaeth offthalmig ym 1960.
Ym maes deintyddiaeth,microsgopau llawfeddygolfe'u cymhwyswyd i driniaeth llenwi ac adfer deintyddol mor gynnar â dechrau'r 1960au yn Ewrop. Cymhwysomicrosgopau gweithredumewn endodonteg ddechreuodd go iawn yn y 1990au, pan adroddodd yr ysgolhaig Eidalaidd Pecora am y defnydd omicrosgopau llawfeddygol deintyddolmewn llawdriniaeth endodontig.
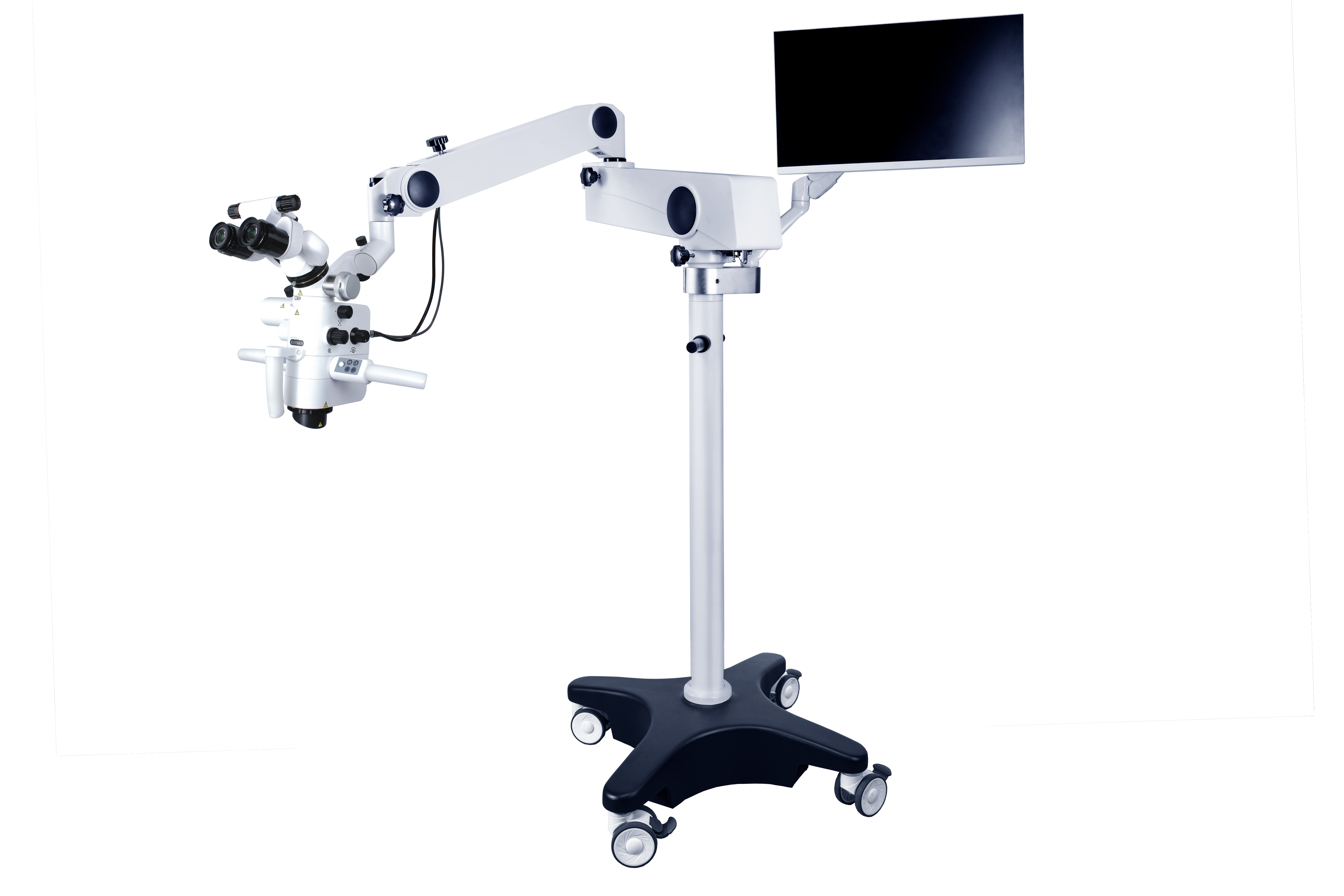
Mae deintyddion yn cwblhau triniaeth clefydau'r pwlp a'r periapical o danmicrosgop gweithredu deintyddolGall y microsgop llawfeddygol deintyddol chwyddo'r ardal leol, arsylwi strwythurau mwy manwl, a darparu ffynhonnell golau ddigonol, gan ganiatáu i ddeintyddion weld strwythur y gamlas wreiddyn a'r meinweoedd periapicol yn glir, a chadarnhau'r safle llawfeddygol. Nid yw bellach yn dibynnu'n llwyr ar deimladau a phrofiad ar gyfer triniaeth, a thrwy hynny'n lleihau ansicrwydd triniaeth ac yn gwella ansawdd triniaeth ar gyfer clefydau pwlpaidd a periapicol yn fawr, gan alluogi rhai dannedd na ellir eu cadw gan ddulliau traddodiadol i dderbyn triniaeth a chadwraeth gynhwysfawr.
A microsgop deintyddolyn cynnwys system oleuo, system chwyddo, system ddelweddu, a'u hategolion. Mae'r system chwyddo yn cynnwys llygadlen, tiwb, lens amcan, addasydd chwyddo, ac ati, sy'n addasu'r chwyddiad gyda'i gilydd.
Cymryd y CORDERMicrosgop llawfeddygol deintyddol ASOM-520-Der enghraifft, mae chwyddiad y llygadlen yn amrywio o 10 × i 15 ×, gyda chwyddiad cyffredin o 12.5X, ac mae hyd ffocal y lens amcan yn yr ystod o 200 ~ 500 mm. Mae gan y newidydd chwyddiad ddau ddull gweithredu: addasiad di-gam trydan ac addasiad chwyddiad parhaus â llaw.
System goleuo'rmicrosgop llawfeddygolyn cael ei ddarparu gan ffynhonnell golau ffibr optig, sy'n darparu goleuo cyfochrog llachar ar gyfer y maes golygfa ac nad yw'n cynhyrchu cysgodion yn ardal y maes llawfeddygol. Gan ddefnyddio lensys binocwlaidd, gellir defnyddio'r ddau lygad ar gyfer arsylwi, gan leihau blinder; Cael delwedd gwrthrych tri dimensiwn. Un dull i ddatrys y broblem cynorthwyydd yw cyfarparu drych cynorthwyol, a all ddarparu'r un olygfa glir â'r llawfeddyg, ond mae cost cyfarparu drych cynorthwyol yn gymharol uchel. Dull arall yw gosod system gamera ar y microsgop, ei chysylltu â sgrin arddangos, a chaniatáu i gynorthwywyr wylio ar y sgrin. Gellir hefyd ffotograffio neu recordio'r broses lawfeddygol gyfan i gasglu cofnodion meddygol ar gyfer addysgu neu ymchwil wyddonol.
Yn ystod triniaeth clefydau'r mwydion a'r periapicwl,microsgopau llawfeddygol deintyddolgellir ei ddefnyddio ar gyfer archwilio agoriadau camlesi gwreiddiau, clirio camlesi gwreiddiau calchaidd, atgyweirio tyllu wal camlesi gwreiddiau, archwilio morffoleg camlesi gwreiddiau ac effeithiolrwydd glanhau, tynnu offerynnau wedi torri a phentyrrau camlesi gwreiddiau wedi torri, a pherfformiomicrolawfeddygolgweithdrefnau ar gyfer clefydau periapicol.
O'i gymharu â llawdriniaeth draddodiadol, mae manteision microlawdriniaeth yn cynnwys: lleoliad manwl gywir apex y gwreiddyn; Mae gan resection llawfeddygol traddodiadol o asgwrn ystod fwy, yn aml yn fwy na neu'n hafal i 10mm, tra bod gan ddinistrio esgyrn microlawfeddygol ystod lai, yn llai na neu'n hafal i 5mm; Ar ôl defnyddio microsgop, gellir arsylwi morffoleg wyneb gwreiddyn y dant yn gywir, ac mae ongl llethr torri'r gwreiddyn yn llai na 10°, tra bod ongl llethr torri'r gwreiddyn traddodiadol yn fwy (45°); Y gallu i arsylwi'r isthmws rhwng camlesi gwreiddyn ar flaen y gwreiddyn; Gallu paratoi a llenwi pennau gwreiddyn yn gywir. Yn ogystal, gall leoli'r tirnodau anatomegol arferol o safle torri'r gwreiddyn a system gamlas y gwreiddyn. Gellir tynnu lluniau neu recordio'r broses lawfeddygol i gasglu data at ddibenion ymchwil clinigol, addysgu neu wyddonol. Gellir ystyried bodmicrosgopau llawfeddygol deintyddolbod â gwerth a rhagolygon cymhwysiad da wrth wneud diagnosis, trin, addysgu ac ymchwil glinigol i glefydau mwydion deintyddol.

Amser postio: 19 Rhagfyr 2024